RNNCell与LSTMCell
单步的RNN
RNNCell
- TF中实现RNN的基本单元 : RNNCell
- 每个RNNCell都有个call方法,每Call一次就做一次运算
(output, next_state) = call(input, state)- 假设有一个初始状态h0与输入x1,调用
call(x1, h0)后就可以得到一个y1和h1 :(y1, h1),以此类推
- RNNCell是一个抽象类,实际上使用的是它的两个子类BasicRNNCell和BasicLSTMCell
- RNNCell的两个类属性
state_size: 隐含层的大小output_size: 输出的大小E.g.假设将一个batch,有batch_size行,input_size列,送入模型计算,那么- 输入数据的形状为(
batch_size,input_size), - 计算时得到的隐含层状态就是(
batch_size,state_size) - 输出是(
batch_size,output_size)
- 输入数据的形状为(
- 每个RNNCell都有个call方法,每Call一次就做一次运算
下面是一个初始化BasicRNNCell的样例代码
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(num_units=128)
# 这里的uum_units = cell.state_size = 128,即隐含层有128个单元
print(cell.state_size) # 128
inputs = tf.placeholder(np.float32, shape=(32, 100))
# placeholder定义输入的Tensor
# 32 是 batch_size,100 是 input_size
# 这里的一份 batch 就是 32 行有 100 列的矩阵
h0 = cell.zero_state(32, np.float32)
# 通过zero_state得到一个全0的初始状态,形状为(batch_size, state_size)
output, h1 = cell.__call__(inputs, h0) #调用call函数
print(h1.shape) # (32, 128)
print(output.shape) # (32, 128)
LSTMCell
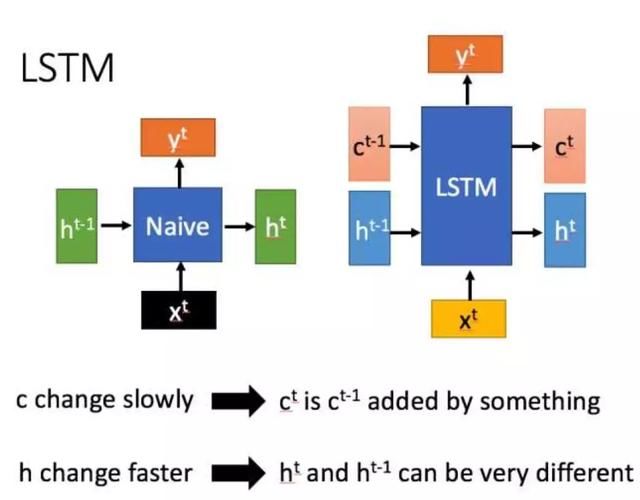
LSTM是一种特殊的循环神经网络,改善了RNN中的梯度消失问题,其和RNN最明显的区别在于,对于特定时刻t,隐藏层输出一个hidden state -> ht和cell state-> ct
所以使用BasicLSTMCell时情况稍有不同,每个h和c的shape都是(batch_size, state_size)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
lstm_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=128)
inputs = tf.placeholder(np.float32, shape=(32, 100)) # 32 是 batch_size
h0 = lstm_cell.zero_state(32, np.float32)
# 通过zero_state得到一个全0的初始状态
output, h1 = lstm_cell.__call__(inputs, h0)
print(h1.h) # shape=(32, 128)
print(h1.c) # shape=(32, 128)
以上为单步RNN,即只调用一次call的情况,每次调用“推进”一个状态。
一次执行多步RNN
Tensorflow提供了一个方法tf.nn.dynamic_rnn,使我们可以通过{h0,x1, x2, …., xn}直接得{h1,h2…,hn}。
设我们输入数据的格式为(batch_size, time_steps, input_size),其中time_steps表示序列本身的长度
# inputs: shape = (batch_size, time_steps, input_size)
# cell: RNNCell
# initial_state: shape = (batch_size, cell.state_size)。初始状态。一般可以取零矩阵
outputs, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, initial_state=initial_state)
此时,得到的outputs就是time_steps步里所有的输出。它的形状为(batch_size, time_steps, cell.output_size)。
state是最后一步的隐状态,它的形状为(batch_size, cell.state_size)。
定义多层RNN
TensorFlow中,可以使用tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell函数对RNNCell进行堆叠
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 每调用一次这个函数就返回一个BasicRNNCell
def get_a_cell():
return tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(num_units=128)
# 用tf.nn.rnn_cell MultiRNNCell创建3层RNN
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([get_a_cell() for _ in range(3)]) # 3层RNN
# 得到的cell实际也是RNNCell的子类
# 它的state_size是(128, 128, 128)
# (128, 128, 128)并不是128x128x128的意思
# 而是表示共有3个隐层状态,每个隐层状态的大小为128
print(cell.state_size) # (128, 128, 128)
# 使用对应的call函数
inputs = tf.placeholder(np.float32, shape=(32, 100)) # 32 是 batch_size
h0 = cell.zero_state(32, np.float32) # 通过zero_state得到一个全0的初始状态
output, h1 = cell.call(inputs, h0)
print(h1) # tuple中含有3个32x128的向量
tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell同样是RNNCell的子类,可以应用多步调用
参考
- 知乎专栏——TensorFlow中RNN实现的正确打开方式
